The Mesopotamia social pyramid is a fascinating aspect of ancient civilization that showcases how society was structured in one of the world's earliest urban centers. Understanding this social hierarchy not only provides insight into the daily lives of the people but also reflects the complexities of governance, economy, and culture in Mesopotamia. In this article, we will explore the different layers of the social pyramid, the roles and responsibilities of each class, and how this structure influenced Mesopotamian society as a whole.
The social pyramid of Mesopotamia is often depicted as a tiered structure, with the ruling class at the top and the laborers at the bottom. This hierarchical system was not just about power; it was also about the distribution of resources, labor, and social responsibilities. Each level of the pyramid played a critical role in the functioning of society, ensuring its stability and growth.
By examining the Mesopotamia social pyramid, we can gain a better understanding of how social stratification impacted various aspects of life, including economics, politics, and culture. This article will delve into the nuances of each class, supported by historical data and references, while also considering the implications of such a structure on the lives of the people who inhabited this ancient region.
Table of Contents
1. Overview of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia, often referred to as the "Cradle of Civilization," is a historical region located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, primarily in modern-day Iraq. This area is known for its early advancements in writing, architecture, and governance. The Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians were some of the key civilizations that thrived in Mesopotamia, each contributing significantly to the development of social structures, including the social pyramid.
In Mesopotamia, agriculture played a pivotal role in the economy. The fertile land supported the growth of crops, leading to surplus production. This surplus allowed the population to grow and led to the emergence of complex social structures, including the hierarchical social pyramid.
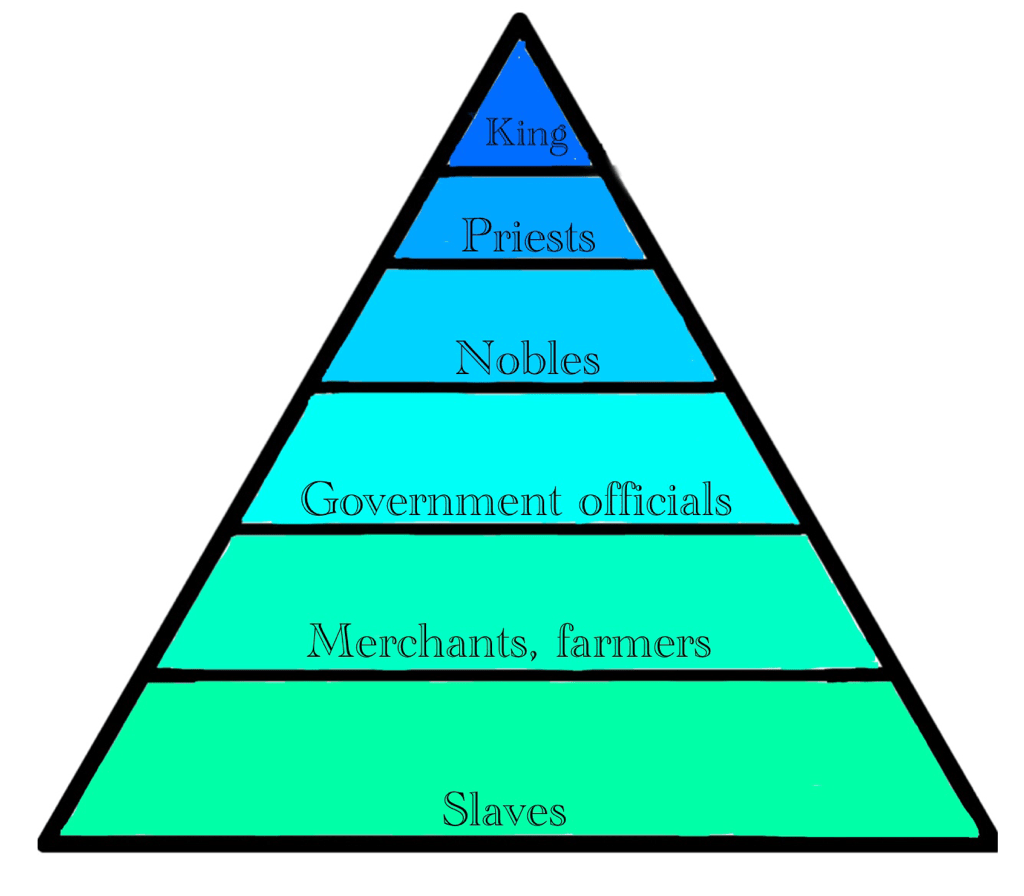
2. The Structure of the Social Pyramid
The Mesopotamia social pyramid can be broadly categorized into four main classes: the ruling class, the priests and religious leaders, the middle class, and the lower class. Each class had its distinct roles and responsibilities, contributing to the overall functioning of society.
2.1 The Four Main Classes
- Ruling Class: This top tier included kings, nobles, and elite individuals who held political power and owned large estates.
- Priests and Religious Leaders: They played a crucial role in society, acting as intermediaries between the gods and the people.
- Middle Class: Comprised of merchants, craftsmen, and skilled laborers who contributed to the economy.
- Lower Class: This group included farmers, laborers, and enslaved individuals who worked the land and performed manual labor.
3. The Ruling Class
The ruling class of Mesopotamia was at the pinnacle of the social pyramid. Kings and nobles not only held political power but also controlled vast agricultural lands and resources. They were responsible for making critical decisions that affected the entire society, including laws, trade, and military actions.
**Key Characteristics:**
- **Political Authority:** Kings ruled with the belief that they were chosen by the gods to govern.
- **Land Ownership:** Nobles owned large estates, which were worked by the lower classes.
- **Wealth and Influence:** The ruling class was often wealthy, allowing them to exert significant influence over various aspects of life.
4. The Priests and Religious Leaders
Priests and religious leaders held significant power in Mesopotamian society, serving as spiritual guides and intermediaries between the gods and the people. They conducted rituals, managed temples, and influenced political decisions.
**Roles of Priests:**
- **Rituals and Ceremonies:** Priests performed essential rituals to appease the gods.
- **Temple Management:** They oversaw the operations of temples, which were central to Mesopotamian life.
- **Advisors to Kings:** Priests often advised rulers on matters of state, intertwining religion and politics.
5. The Middle Class
The middle class in Mesopotamia consisted of merchants, artisans, and skilled laborers. This class played a vital role in the economy, as they were responsible for trade, craftsmanship, and the production of goods.
**Importance of the Middle Class:**
- **Economic Growth:** The middle class was crucial for the development of trade and commerce.
- **Social Mobility:** Individuals in this class had the potential to rise in status through wealth and skill.
- **Cultural Contributions:** Artisans and craftsmen contributed significantly to the cultural heritage of Mesopotamia.
6. The Lower Class and Laborers
The lower class, comprising farmers, laborers, and enslaved individuals, formed the base of the social pyramid. They were essential for agricultural production and manual labor, supporting the economy and society.
**Features of the Lower Class:**
- **Labor Intensive:** Most individuals in this class worked long hours in agriculture or construction.
- **Limited Rights:** They had few rights and were often subject to the whims of the ruling class.
- **Enslavement:** Some individuals were enslaved, either through conquest or debt, and had no personal freedoms.
7. The Impact of the Social Structure
The social pyramid of Mesopotamia profoundly impacted every aspect of life. It influenced governance, economic stability, and cultural practices. The hierarchical structure created a clear division of labor and responsibilities, which was essential for managing complex societies.
**Consequences of the Social Pyramid:**
- **Stability and Order:** The structured hierarchy contributed to political stability.
- **Cultural Development:** Each class had its cultural practices and traditions, enriching Mesopotamian culture.
- **Economic Functionality:** The division of labor allowed for specialization, which boosted economic productivity.
8. Conclusion and Reflection
In conclusion, the Mesopotamia social pyramid illustrates the complexities of ancient societal structures. Each class played a specific role, contributing to the overall stability and growth of this influential civilization. Understanding this social hierarchy not only provides insight into Mesopotamian life but also helps us appreciate the foundations of modern social structures.
We encourage you to reflect on how these ancient societal models have influenced contemporary culture and governance. Feel free to leave your thoughts in the comments below, share this article with others, and explore more about ancient civilizations on our site!
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to welcoming you back for more enlightening discussions on history and culture.
ncG1vNJzZmirn521b6%2FOpmatoJWovKm01qarp52nqIBwucSspqmnpJa6qq2MrKacoZGherHF0ZqkopxencGuuA%3D%3D